10.2.1 What is Accreditation?
Accreditation is the official recognition by the Bureau of the International Coordinating Committee of National Institutions (ICC Bureau) that a national institution meets or continues to comply fully with the Paris Principles. National Institutions may be afforded the following accreditation Statuses:
A Voting Member: full compliance with the Paris Principles.
B Observer Member: not fully in compliance with the Paris Principles or has not yet submitted sufficient documentation to make that determination.
C Non-member: is non-compliant with the Paris Principles.
A-Status institutions can participate fully in the work and meetings of National Institutions internationally and regionally as a voting member, and they can hold office in the ICC Bureau or any Sub-Committee established by the Bureau. A-status institutions are also able to participate in HRC sessions and take the floor under any agenda item, submit documentation and take separate seating.
B-Status institutions may participate as observers in the work and meetings of national institutions nationally and regionally. They cannot vote or hold office within the ICC Bureau or its Sub-Committees. They are not given NHRI badges, nor may they take the floor under agenda items and submit documentation in the HRC.
C-Status institutions have no rights or privileges with the Network or in UN rights fora. They may, at the invitation of the Chairperson of the Bureau, attend meetings of the ICC.
The ICC
At the 1993 International Conference held in Tunis, NHRIs established the International Coordinating Committee of National Institutions for the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights (ICC). It was aimed at coordinating the activities of the NHRI network. In 2008, the ICC was incorporated under Swiss law, with a Bureau of 16 voting members representing the four regions of the ICC. The ICC also adopted the ICC Statute as a basis for the incorporation.
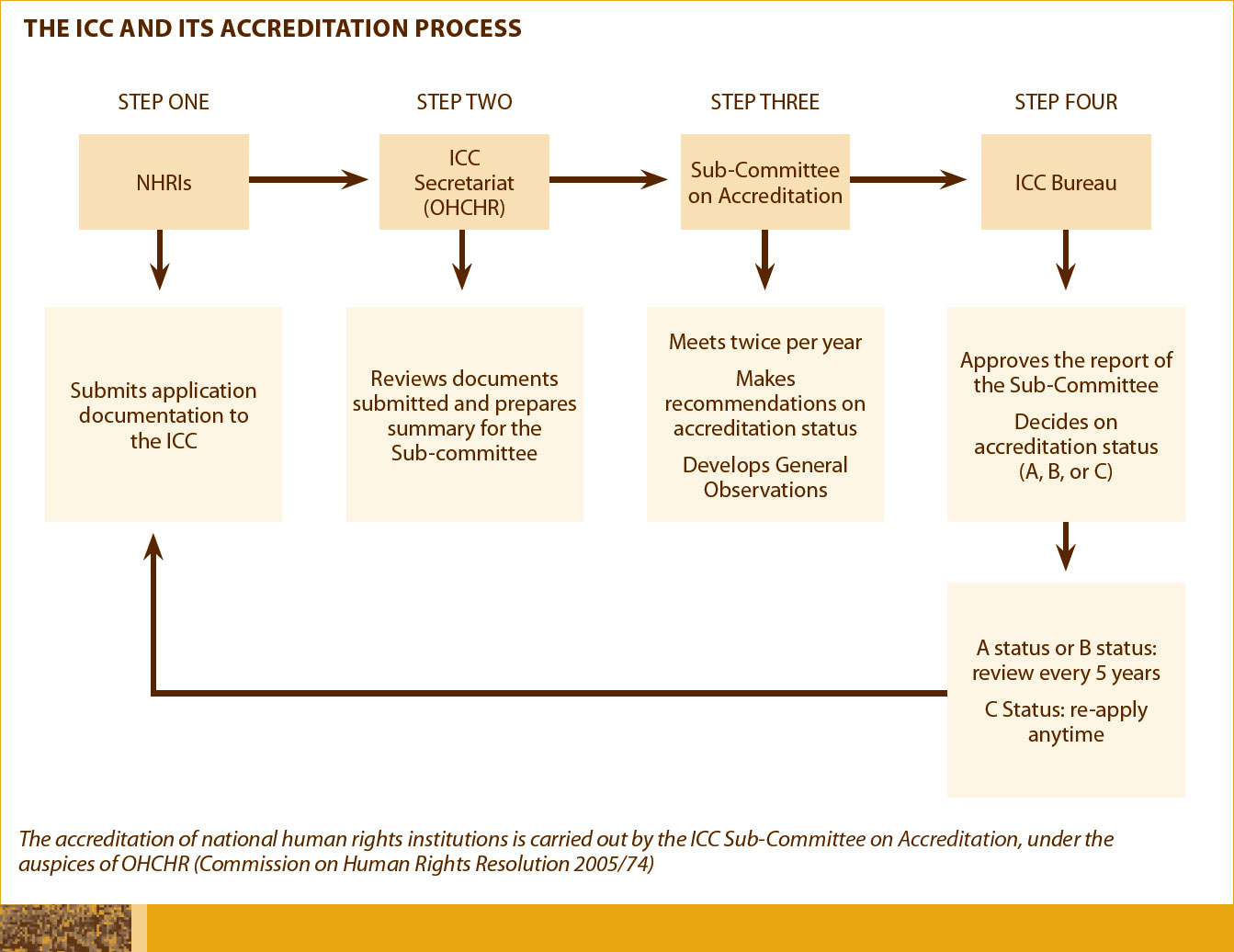
The ICC Sub-Committee on Accreditation
The Sub Committee on Accreditation (SCA) of the ICC reviews and analyzes accreditation applications and makes recommendations to ICC Bureau members on compliance with the Paris Principles. The SCA is composed of one "A status" accredited NHRI for each of the four regional groupings; namely Africa, the Americas, the Asia Pacific, and Europe. Members of the SCA are appointed by the regional groupings for a renewable term of three years. OHCHR participates in the SCA as a permanent observer and as ICC secretariat.
For an overview of the process currently utilized by the SCA of the ICC to accredit national human rights institutions in compliance with the Paris Principles, and its centrality to the UN, see the Annual Reports of The UN High Commissioner For Human Rights and Reports of The Office of the High Commissioner and The Secretary-General, A/HRC/7/70 18 January 2008; 26 January 2009 A/HRC/10/55.
An NHRI can receive any of the following 3 statuses; (1) "A status": compliant with the Paris Principles; (2) "B status"; observer status - not fully in compliance with the Paris Principles or insufficient information provided to make a determination; and (3) "C status"; not compliant with the Paris Principles. As at June 2009, there were 66 NHRIs accredited with A Status by the ICC, i.e. in compliance with the Paris Principles. Summaries of NHRIs that been accredited are available through www.nhri.net.